Today, sustainability in construction is a vital topic for the US market because people want to see positive changes in the approach and development of construction. According to a report by Willmot Dixon, construction industries are liable for causing 40% of drinking water pollution and half of all landfill waste quarterly.
Therefore, informed consumers are demanding greener construction innovation. Due to these demands, construction industries are adopting and transforming their conventional construction practices into greener and more sustainable ones to remain viable and competitive in rapidly transforming construction for a better future.
This article will explore sustainability in construction, discuss its significance for the industry, and review sustainable construction practices. Efficient buildings and structures are at the core of sustainable construction, and renewable products and materials are used.
Why Sustainability in Construction Matters
Reducing Carbon Footprint
The construction sector is one source of greenhouse gas emissions, as many activities require intensive energy and material production. Around the world, buildings contribute to 39% of yearly carbon emissions. This includes two types of carbon: operational carbon, which is the carbon released from everyday use of a building, and embodied carbon, which comes from the carbon emitted during the building process, such as making, transporting, and disposing of construction materials.
A study submitted by Dodge Construction Network states that more than 90% of US E&C companies receive requests from customers to lower the amount of embodied carbon used in construction projects. Sustainable practices entail utilizing renewable energy resources, decreasing resource use, and embracing materials with minimal carbon emissions.
Conserving Resources
Materials from nature like water, timber, and minerals are finite. Sustainability in construction focuses on the reuse of materials and the efficient use of resources in its construction. Deriving resources from conservation and seeking innovative materials to use in construction.
Enhancing Livability
Green buildings ensure that the occupants end up in healthier spaces by having better air quality, letting in natural light, and practicing efficient energy use. It also helps improve occupants’ comfort while utilizing less energy or power.
Meeting Regulatory Standards
Governments in the US continue to implement stricter measures to reduce environmental depletion. Implementing and conforming to sustainability in construction standards reduces legal implications while addressing the need for eco-friendly innovations.
Also Read: The Ultimate Guide to Construction Waste Management and Sustainability
Innovations Shaping Sustainability in Construction

The drive towards sustainability has spurred numerous innovations in construction practices and technologies. Here are some key areas where significant advancements are being made:
1. Green Building Materials
Recycled steel, bamboo, and reclaimed wood are just a few examples of green building materials that have become widely used. Such materials lower wastage and reduce the environmental effects of extracting and processing new resources.
2. Energy-Efficient Designs
Energy efficiency is one of the most important elements in implementing sustainability in construction. This involves appropriately positioning buildings for adequate natural lighting, proper insulation, well-insulated windows, and HVAC systems. These elements greatly help minimize energy use throughout a structure’s life cycle.
3. Embrace Technologies
Technological advancements play a crucial role in enhancing sustainability in construction. Key technologies include:
- Building Information Modeling (BIM): By creating digital prototypes of physical structures, BIM helps plan and manage resources efficiently without creating numerous entities to prevent wastage.
- 3D Printing: Integrating 3D printing in construction reduces the wastage of materials and shortens the project’s completion timelines. Using this technology, we can decide the precise amount of material to use. Transportation costs are also reduced, and sustainability in construction is achieved through energy-efficient designs and structures.
- Internet of Things (IoT): It measures power consumption, tracks construction resource use, and identifies real-time inefficiencies. Advanced sensors embedded in buildings offer essential information to enhance resource energy efficiency.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning: For sustainability in construction management, AI-driven tools analyze data to optimize construction processes. With these tools, project managers can mitigate risk before it becomes severe. Machine learning boosts project management, optimizes resource needs, and reduces waste.
- Green Building Certifications: Recognitions like LEED (Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design) or BREEAM (Building Research Establishment Environmental Assessment Method) enable a framework for evaluating sustainability in building construction. These certifications promote developers’ use of sustainable development in their projects.
- Renewable Energy Systems: Renewable power systems, such as solar panels, wind turbines, and geothermal heat, are used in construction projects to decrease the use of conventional energy resources. These systems promote sustainability in construction.
- Project Management Information System: PMIS such as e-Builder improves sustainability in construction by increasing the effectiveness of monitoring capital projects and allocating resources and workflow. A cloud-based practice can significantly improve decision-making, as every resource can be optimized, reducing waste.
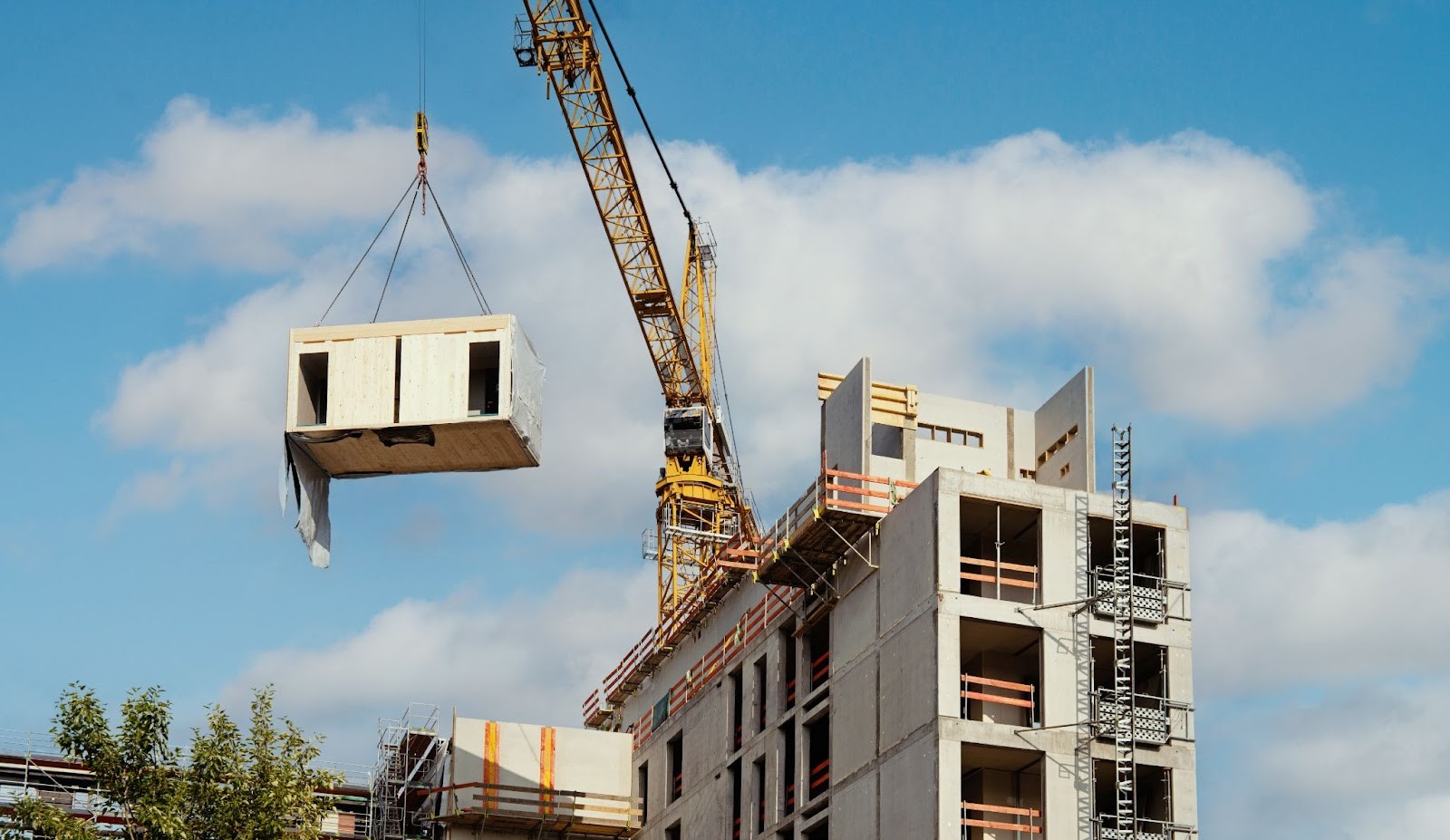
4. Modular and Prefabricated Construction
Modular construction is constructing parts off-site and then taking them to its final location. This method helps cut costs since it minimizes wastage and time. This allows control over materials usage and promotes sustainability in construction methods.
5. Waste Reduction and Circular Economy
The circular economy concept in construction aims to utilize materials and reduce waste. Strategies such as on-site recycling, salvaging materials, and designing for deconstruction help reduce waste and promote sustainability in construction projects.
6. Water Conservation Technologies
Water conservation technologies include rainwater harvesting, greywater recycling, and low-flow fixtures. These help save water and manage it effectively throughout the lifecycle of sustainable construction and capital projects.
Challenges in Achieving Sustainability in Construction
Despite the clear benefits of sustainable construction practices, several challenges hinder widespread adoption:
1. Cost Barriers
The high initial cost is one of the most significant drawbacks of using sustainable materials and technologies. This keeps many developers from adopting sustainable construction technologies even though such investments lead to long-term profits.
2. Lack of Awareness
The principles of sustainability in construction are still unfamiliar to builders, developers, and consumers. It is necessary to carry out promotional activities to introduce stakeholders to the potential benefits of implementing sustainable measures in capital projects.
3. Limited Access to Green Materials
Sustainable materials are available based on geographical area or market availability only. This scarcity can hamper the attempts to drive effective adoption of green building practices in the construction industry.
Conclusion
Sustainability in construction is not a trend but it’s a fundamental shift towards a better and green future in construction industries. Focusing on the application of innovative materials, energy-efficient design, BIM, IoT, and renewable energy systems, change is driving the industry. By prioritizing sustainability, the construction sector can significantly reduce its environmental footprint, conserve resources, and enhance livability for future generations.
Do you want to reduce carbon emissions in your next capital project? Get in touch with OnIndus to integrate Sustainability in construction through technologies like BIM and PMIS, enhancing efficiency, resource optimization, and project success.